Rivers of India Static GK / General Awareness for Competitive Exams (2026) + Memory Tricks
This post covers Rivers of India with origin, length, tributaries, and end-point—exactly how questions appear in SSC GK, IBPS, Railways, UPSC Prelims, Defence and other Govt exams. Includes revision tables, mnemonics, “don’t confuse” traps, and PYQ patterns.
Jump to section
- INTRODUCTION
- 1) Types of River Systems in India (Most Asked Concept)
- 2) Top 10 Longest Rivers in India (Most Repeated GK List)
- 3) The “Top 5 Most Asked Rivers” (SSC/Banking/UPSC Prelims)
- 4) Mega Revision List (From Your Given Content) — Categorized, Not Flat
- 4A) Ganga Basin & Associated Rivers (North India)
- 4B) Indus Basin Rivers (North-West & Transboundary)
- 4C) Brahmaputra Basin (North-East)
- 4D) Major Peninsular Rivers (East-Flowing → Bay of Bengal)
- 4E) Major West-Flowing & Coastal Rivers (Arabian Sea / Lakshadweep Sea)
- 5) EXAM-FRIENDLY “TRAPS” (Tributaries & Terms)
- Previous Year Questions (PYQ) Analysis: How Rivers of India was asked in last few years
- THE “STICKY” MEMORY ZONE: Rivers Mnemonics That Actually Work
- Don’t Mix These Up in Exams (High-Confusion Pairs)
- KEY POINTS / IMPORTANT FEATURES (Most Important for Exams)
- ADDITIONAL NOTES (Tricky but Useful)
- IMPORTANT ONE-LINERS FOR SSC/Banking/UPSC Prelims
- QUICK-SUMMARY TABLE (Most Asked → Direct Answers)
INTRODUCTION
A river system means a main river plus its tributaries/distributaries and drainage basin. In Govt exams, questions are rarely theoretical—mostly match the following, origin–mouth, right/left bank tributary, delta vs estuary, and “nickname” type facts.
This topic is repeatedly asked in SSC CGL/CHSL/GD, IBPS PO/Clerk, RRB NTPC/Group D, UPSC Prelims, CAPF/Defence, and State PCS because these facts are mostly static (don’t change).
Key official references used for exam - standard facts include Press Information Bureau, National Mission for Clean Ganga, and Ministry of External Affairs sources.
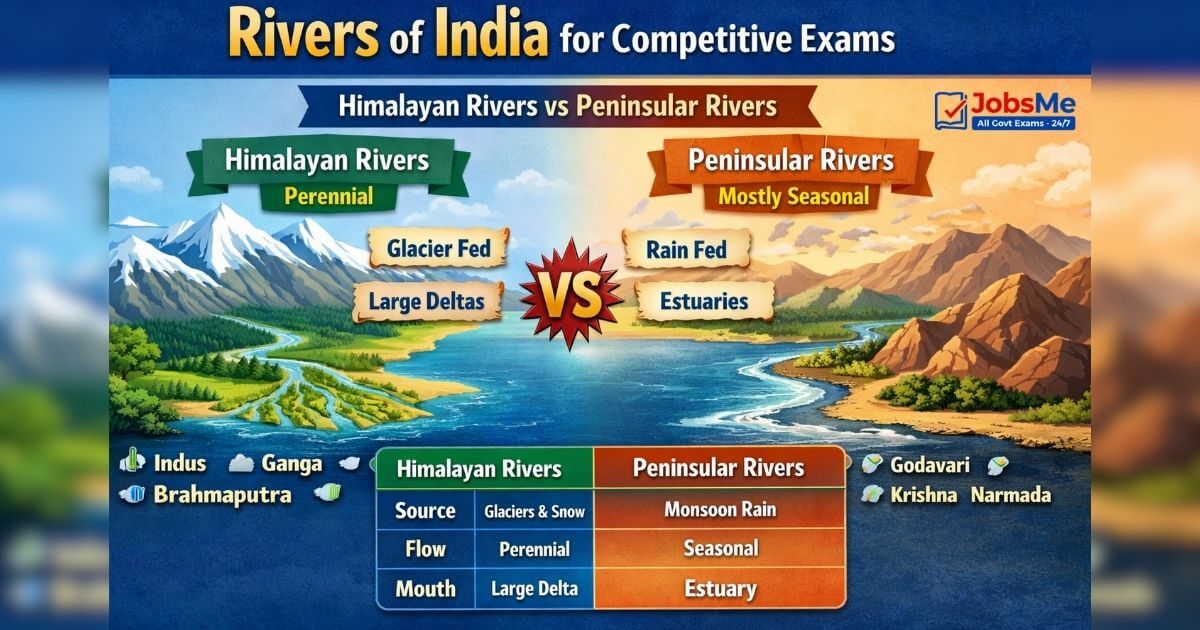
1) Types of River Systems in India (Most Asked Concept)
A) Himalayan Rivers (Perennial)
- Mostly snow/glacier-fed, flow throughout the year.
- Form wide floodplains and large deltas (e.g., Ganga–Brahmaputra delta region).
B) Peninsular Rivers (Mostly seasonal)
- Mostly rain-fed (monsoon), comparatively shorter and less water volume.
- Many flow east to Bay of Bengal forming deltas; major west-flowing rift-valley rivers form estuaries.
Side-by-Side Comparison Table (High-Frequency)
| Feature | Himalayan Rivers | Peninsular Rivers |
|---|---|---|
| Water source | Glacier/snow + rain | Mostly monsoon rain |
| Flow nature | Perennial | Often seasonal |
| Landform | Broad plains, heavy silt | Plateau & hard rock |
| Mouth feature | Big deltas common | Many deltas (east); estuaries (west) |
| Examples | Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra | Godavari, Krishna, Cauvery, Narmada, Tapi |
Why asked in SSC/Railways? Because they love 1-liners like: “Himalayan rivers are perennial” and “Narmada forms an estuary, not delta.”
2) Top 10 Longest Rivers in India (Most Repeated GK List)
What this table covers: exam-standard “length in India vs total length”, plus origin and outfall (frequent match questions).
| Rank | River | Length in India (km) | Total length (km) | Origin (exam-ready) | Empties into |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ganga | ~2525 | ~2525 | Gangotri Glacier | Bay of Bengal |
| 2 | Godavari | ~1465 | ~1465 | Trimbak area | Bay of Bengal |
| 3 | Krishna | ~1400 | ~1400 | Mahabaleshwar (Western Ghats) | Bay of Bengal |
| 4 | Yamuna | ~1376 | ~1376 | Yamunotri Glacier | Ganga at Sangam |
| 5 | Narmada | ~1312–1315 | ~1312–1315 | Amarkantak | Arabian Sea (estuary) |
| 6 | Indus | ~1114 | ~3180 | Tibet (near Kailash region) | Arabian Sea |
| 7 | Brahmaputra | ~916 | ~2900 | Angsi Glacier region | Bay of Bengal (via system) |
| 8 | Mahanadi | ~858 | ~858 | Chhattisgarh region | Bay of Bengal |
| 9 | Cauvery (Kaveri) | ~800 | ~800 | Talakaveri | Bay of Bengal |
| 10 | Tapi (Tapti) | ~724 | ~724 | Satpura ranges | Gulf of Khambhat |
Notes used for verification (Govt/standard references): Ganga length & course ; Yamuna length ; Krishna & Cauvery basin references ; Brahmaputra length in India ; Narmada estuary (rift valley) ; Indus total length varies but commonly ~3180 km .
3) The “Top 5 Most Asked Rivers” (SSC/Banking/UPSC Prelims)
3.1 Ganga (National River)
- Declared National River on 4 Nov 2008 (asked as a direct fact).
- Length: ~2525 km; rises from Gangotri Glacier and flows to Bay of Bengal.
- Key headstreams: Bhagirathi + Alaknanda meet at Devprayag (classic match question).
- Big exam trap: Hooghly is a major distributary/connected channel in West Bengal region (often miscalled a tributary).
- Famous bridges asked in Static GK: Mahatma Gandhi Setu is over Ganga.
Why asked in SSC/Railways? National River + longest-in-India + tributary list (Yamuna, Ghaghara, Gandak, Kosi, Son).
3.2 Godavari (Dakshin Ganga)
- Called Dakshina Ganga / Southern Ganga (nickname questions).
- Length: ~1465 km, major peninsular river; empties into Bay of Bengal.
- Important tributaries often asked: Pranhita, Indravati, Manjira, Wainganga, Penganga/Sabari (vary by source list).
3.3 Brahmaputra (NE Lifeline)
- Names are a favorite trick: Tsangpo/Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibet, and Jamuna in Bangladesh.
- Total length ~2900 km; in India ~916 km (asked as “length in India”).
- Majuli is a famous river island in Assam on Brahmaputra (often asked in UPSC/State PCS).
- Bridge GK: Saraighat Bridge crosses Brahmaputra.
3.4 Yamuna (Largest tributary of Ganga by length)
- Origin: Yamunotri Glacier; length ~1376 km; meets Ganga at Triveni Sangam in Prayagraj.
- Right-bank tributaries commonly asked: Chambal, Betwa, Ken.
3.5 Kaveri/Cauvery (South India’s holy river)
- Origin: Talakaveri in Brahmagiri range; total length commonly taken as ~800 km.
- Tributaries asked in exams: Kabini, Hemavati, Bhavani, Amaravati, Noyyal.
4) Mega Revision List (From Your Given Content) — Categorized, Not Flat
Abbreviation Key (for tables)
UK=Uttarakhand, UP=Uttar Pradesh, BR=Bihar, WB=West Bengal, MP=Madhya Pradesh, MH=Maharashtra, HP=Himachal Pradesh, J&K=Jammu & Kashmir, LA=Ladakh, CG=Chhattisgarh, OD=Odisha, JH=Jharkhand, KA=Karnataka, TN=Tamil Nadu, KL=Kerala, GJ=Gujarat, RJ=Rajasthan, TS=Telangana, AP=Andhra Pradesh
4A) Ganga Basin & Associated Rivers (North India)
What this table covers: the Ganga system rivers from your list—highly asked in SSC “river → tributary/mouth” matches.
| River | Origin (as given) | Length (km) | Ends / Meets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ganga | Gangotri Glacier (Bhagirathi), UK | 2525 | Bay of Bengal |
| Yamuna | Yamunotri Glacier, UK | 1376 | Meets Ganga at Prayagraj |
| Chambal | Tributary of Yamuna; starts MP | 960 | Joins Yamuna (UP) |
| Son | Amarkantak, MP | 784 | Joins Ganga near Patna |
| Gandak | Nepal (Indo-Nepal border) | 630 | Joins Ganga near Patna |
| Kosi | Indo-Nepal border (BR region) | 720 | Joins Ganga near Katihar |
| Betwa | Vindhya region, MP | 590 | Joins Yamuna at Hamirpur |
| Gomti | Gomat Taal, UP | 900 | Joins Ganga (Varanasi dist.) |
| Ghaghara | Himalayan glacier (Tibet) | 1080 | Joins Ganga (BR) |
| Hugli/Hooghly | Ganga distributary (WB) | 260 | Bay of Bengal |
| Damodar | Jharkhand (Chandwara area) | 592 | Meets Hooghly (WB) |
| Mahananda | Paglajhora falls, Darjeeling (WB) | 360 | Meets Ganga |
| Alaknanda | Satopanth & Bhagirathi-Kharak glaciers | 190 | Meets Bhagirathi at Devprayag |
| Bhagirathi | Gaumukh, UK | 205 | Meets Alaknanda at Devprayag |
Why is it famous / asked?
- Kosi = “Sorrow of Bihar” (floods) is a classic one-liner.
- Damodar = “Sorrow/River of Sorrows (Bengal)” (historic floods).
4B) Indus Basin Rivers (North-West & Transboundary)
| River | Origin (as given) | Length (km) | Ends / Meets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indus | Tibetan plateau; enters J&K | 3180 | Arabian Sea near Sindh |
| Chenab | Upper Himalayas (HP/region) | 960 | Meets Indus |
| Jhelum | Tributary of Chenab (Punjab/region) | 725 | Meets Chenab at Jhang (Pakistan) |
| Ravi | Bara Bhangal (HP) | 720 | Joins Chenab (Pakistan) |
| Sutlej | Rakshastal (Tibet) | 1500 | Meets Beas; ultimately Arabian Sea system |
| Beas | Central HP Himalayas | 470 | Joins Sutlej (Punjab) |
| Parbati | Mantalai Glacier | — | Meets Beas at Bhuntar |
| Suru | Panzella Glacier, Pensi La (Kargil) | 185 | Meets Indus (Pakistan region) |
| Dras | Machoi Glacier, Zoji La | 86 | Meets Suru at Kharul |
| Zanskar | Doda + Kargyag/Tsarap branches | — | Meets Indus near Nimmu (LA) |
| Tsarap | Pankpo La, Sarchu | 182 | Meets Zanskar at Padum |
| Doda | Drang-Drung Glacier, Pensi La | 79 | Meets Zanskar at Padum |
Indus Water Treaty (1960) – Super High Yield
- Eastern Rivers: Ravi, Beas, Sutlej
- Western Rivers: Indus, Jhelum, Chenab
Why asked in UPSC/Defence/SSC? Because MCQs directly ask “Which of the following are Western rivers?” or “Arrange treaty rivers.”
4C) Brahmaputra Basin (North-East)
| River | Origin (as given) | Length (km) | Ends / Meets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brahmaputra | Himalayan glacier in Tibet; enters Arunachal | 1800 (given) | Meets Ganga system → Bay of Bengal |
Exam note: Many sources quote ~2900 km total and ~916 km in India (the “in India” line is a frequent trap).
4D) Major Peninsular Rivers (East-Flowing → Bay of Bengal)
| River | Origin (as given) | Length (km) | Ends / Meets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kaveri | Talakaveri (Western Ghats), KA | 765 | Bay of Bengal |
| Krishna | Western Ghats near Mahabaleshwar (MH) | 1400 | Bay of Bengal |
| Godavari | Starts in MH; 7 states | 1465 | Bay of Bengal |
| Tungabhadra | Tributary of Krishna (KA) | 531 | Joins Krishna (TS–AP border) |
| Indravati | Dandakaranya range (OD) | 535 | Joins Godavari |
| Pranhita | Wardha + Wainganga confluence | 113 | Joins Godavari near Kaleshwaram |
| Wardha | Satpura (Multai/MP) | 528 | Joins Pranhita |
| Kolab (Sabari) | Sinkaran hills (OD) | 200 | Joins Godavari |
| Manjira | Balaghat hills | 724 | Joins Godavari |
| Wainganga | Satpura (Seoni/MP) | 579 | Joins Pranhita |
| Painganga | Ajanta range (MH) | 676 | Joins Wardha |
| Vedavathi | Veda + Avathi confluence | — | Joins Tungabhadra |
| Bhima | Bhimashankar | 861 | Joins Krishna |
| Indrayani | Lonavala (MH) | — | Joins Bhima |
| Pavana | Sahyadri range (MH) | 58 | Joins Mula |
| Ghataprabha | Western Ghats (MH) | 283 | Joins Krishna |
| Venna | Mahabaleshwar | 130 | Joins Krishna |
| Koyna | Mahabaleshwar | 130 | Joins Krishna |
| Amravati | Anamalai hills | 282 | Joins Kaveri at Karur |
| Bhavani | Silent Valley (KL) | 135 | Joins Kaveri |
| Hemavati | Western Ghats (KA) | 245 | Joins Kaveri near KRS |
| Mahanadi | Dhamtari/CG | 858 | Bay of Bengal (Odisha coast) |
| Subarnarekha | Chota Nagpur plateau (JH) | 395 | Bay of Bengal |
| Kangsabati | Chota Nagpur plateau (WB) | 465 | Bay of Bengal near Haldia |
| Penner (Penna) | Nandi Hills (KA) | 597 | Bay of Bengal near Nellore |
| Palar | Nandi hills (KA) | 348 | Bay of Bengal (TN) |
| Vaigai | Varusanadu Hills (TN) | 258 | Palk Strait |
| Vellar | Shevaroy Hills | 150 | Bay of Bengal |
| Ponnaiyar | Nandidurg | 400 | Bay of Bengal |
| Noyyal | Velliangiri Hills | 180 | Joins Kaveri |
Why asked in exams?
- Hirakud Dam is on Mahanadi (very common).
- “Krishna flows through multiple states + major tributaries” is frequent in UPSC/State PCS.
4E) Major West-Flowing & Coastal Rivers (Arabian Sea / Lakshadweep Sea)
| River | Origin (as given) | Length (km) | Ends / Meets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tapti (Tapi) | Eastern Satpura (MP) | 724 | Gulf of Khambhat (GJ) |
| Mahi | MP | 580 | Arabian Sea (via GJ) |
| Narmada | Amarkantak (MP) | 1315 | Arabian Sea via Gulf of Khambhat |
| Gomai | Satpura range | — | Tapti |
| Panzara | Dhule (MH) | — | Tapti |
| Purna | Satpura range (MP) | — | Tapti |
| Kolar | Vindhya (MP) | 101 | Narmada |
| Tawa | Satpura range (MP) | 172 | Narmada |
| Sabarmati | Dhebar lake/Aravalli (RJ) | 371 | Gulf of Khambhat |
| Zuari | Western Ghats | 34 | Arabian Sea |
| Ulhas | Rajmachi hills/Sahyadri | 122 | Vasai creek (Mumbai) |
| Mithi | Vihar & Powai lakes | 15 | Arabian Sea (Mahim creek) |
| Mandovi | Bhimgad (KA) | 77 | Arabian Sea |
| Kali | Kushavali (KA) | 184 | Arabian Sea |
| Netravati | Kudremukh (KA) | — | Arabian Sea near Mangalore |
| Sharavati | Western Ghats (KA) | 128 | Arabian Sea near Honnavar |
| Periyar | Sivagiri hills | 244 | Lakshadweep Sea |
| Bharathappuzha | Anamalai Hills | 209 | Lakshadweep Sea (Ponnani) |
| Pamba | Pulachimalai Hills | 176 | Vembanad Lake |
| Chaliyar | Wayanad hills | 169 | Lakshadweep Sea |
Most important concept here: Narmada is a rift-valley river and forms an estuary (not a delta).
5) EXAM-FRIENDLY “TRAPS” (Tributaries & Terms)
Left Bank vs Right Bank (How SSC twists it)
Rule: Face downstream (towards mouth). Your left hand = left bank.
Examples students mix up:
- Ganga left bank: Gomti, Ghaghara, Gandak, Kosi, Mahananda (common lists).
- Ganga right bank: Yamuna, Son (commonly asked).
Why asked? SSC loves statement-based questions like:
“(i) Gomti is a left-bank tributary of Ganga (ii) Son is a left-bank tributary of Ganga.”
Previous Year Questions (PYQ) Analysis: How Rivers of India was asked in last few years
(Observed patterns across SSC/Railways/State PCS papers)
- Match the Following (Most common):
- River ↔ Origin (glacier/hills)
- River ↔ Mouth (Bay of Bengal/Arabian Sea/another river)
- Statement-based (Increasing trend):
- “Narmada forms delta” (False; it forms estuary)
- “Brahmaputra is called Jamuna in Bangladesh” (True)
- One-liner direct facts:
- “National River of India” (Ganga)
- “Sorrow of Bihar/Bengal” (Kosi/Damodar)
- Treaty-based static GK (UPSC/Defence):
- Indus Water Treaty: Eastern vs Western rivers
THE “STICKY” MEMORY ZONE: Rivers Mnemonics That Actually Work
Mnemonics reduce silly errors in last-minute revision (Banking/SSC speed tests).
- “GYB = Golden Yearly Basics”
→ Helps remember top Himalayan trio: Ganga–Yamuna–Brahmaputra. - “Go-Kri-Cau-Mah = Go Crack Mains”
→ Godavari–Krishna–Cauvery–Mahanadi (major peninsular east-flowing rivers). - “Na-Ta = No Delta!”
→ Narmada + Tapi are famous west-flowing rivers; remember estuary, not delta. - “Ra-Be-Su = Treaty Set”
→ Indus Treaty Eastern rivers: Ravi–Beas–Sutlej.
Don’t Mix These Up in Exams (High-Confusion Pairs)
- Don’t confuse Yamuna (Ganga tributary in North India) with Jamuna (name used for Brahmaputra in Bangladesh).
- Don’t confuse Ghaghara (Ganga tributary) with Ghaggar (different river, often linked to Saraswati debates).
- Don’t confuse Hooghly (distributary/connected channel of Ganga) with a normal “tributary”.
- Don’t confuse Tapti/Tapi (same river name variants) with Tawa (a tributary of Narmada in MP).
- Don’t confuse Amaravati River (Cauvery tributary) with Amaravati city (in Andhra Pradesh, near Krishna region).
- Don’t confuse Indravati (Godavari tributary) with Indrayani (Bhima tributary).
- Don’t confuse Kosi (Sorrow of Bihar) with Koyna (Krishna tributary).
- Don’t confuse Damodar (flood-prone “River of Sorrows”) with Mahanadi (Hirakud Dam).
KEY POINTS / IMPORTANT FEATURES (Most Important for Exams)
- Longest river in India (fully within India): Ganga (~2525 km).
- National River: Ganga (declared 4 Nov 2008).
- Largest peninsular river: Godavari (called Dakshin Ganga).
- Rift valley + estuary (not delta): Narmada (and commonly Tapi).
- Kosi nickname: Sorrow of Bihar.
- Damodar nickname: “River of Sorrows” in Bengal region (historic floods).
- Major bridge GK: Mahatma Gandhi Setu over Ganga; Vidyasagar Setu over Hooghly; Saraighat Bridge over Brahmaputra.
- Indus Treaty rivers list is a UPSC/Defence favourite.
ADDITIONAL NOTES (Tricky but Useful)
- River length values vary by source (measurement method differs). In exams, prefer standard rounded figures (e.g., Ganga 2525, Yamuna 1376, Krishna 1400).
- “In India length” vs “Total length” is a common trap for Indus and Brahmaputra.
IMPORTANT ONE-LINERS FOR SSC/Banking/UPSC Prelims
- Ganga is the National River of India (declared 4 Nov 2008).
- Yamuna originates at Yamunotri Glacier and meets Ganga at Triveni Sangam.
- Godavari is called Dakshin Ganga.
- Brahmaputra is called Tsangpo in Tibet and Jamuna in Bangladesh.
- Narmada forms an estuary, not a delta (rift valley river).
- Kosi is the Sorrow of Bihar due to floods.
- Damodar was historically called the “River of Sorrows” in Bengal region.
- Hirakud Dam is built on the Mahanadi River.
- Indus Water Treaty: Eastern rivers = Ravi, Beas, Sutlej.
- Vidyasagar Setu is over the Hooghly River near Kolkata–Howrah.
Ultra-short Revision Bullets (for last 5 minutes)
- Na-Ta = estuary
- Ra-Be-Su = treaty east
- Kosi = Bihar sorrow
- Ganga = 2525 + national
QUICK-SUMMARY TABLE (Most Asked → Direct Answers)
| Most Asked Point | Answer / Fact | Exam Relevance (SSC/UPSC/Banking/etc.) |
|---|---|---|
| National River | Ganga | SSC/Railways |
| Declaration date | 4 Nov 2008 | SSC/State PCS |
| Longest in India | Ganga (~2525 km) | Banking/SSC |
| Largest peninsular river | Godavari | SSC/UPSC |
| Estuary, not delta | Narmada | UPSC/SSC |
| Indus Treaty – Eastern | Ravi–Beas–Sutlej | UPSC/Defence |
| Indus Treaty – Western | Indus–Jhelum–Chenab | UPSC/Defence |
| Sorrow of Bihar | Kosi | SSC/RRB |
| Sorrow of Bengal | Damodar | SSC/State PCS |
| Hirakud Dam river | Mahanadi | SSC/State PCS |
Free quiz • No signup required
Put this topic into practice with Indian Cultural Institutions – Static GK MCQ Quiz. It is the quickest way to reinforce what you just learned.








